Medical Assistant
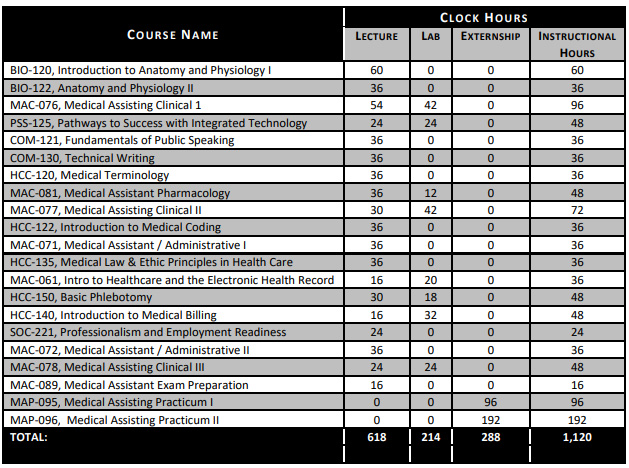
11 Months – Total Clock Hours: 1,120
2026 – 2027 Tuitions Fees: $13,388
Start date: 8/17/2026
Admission Requirements
Application Fee, Application for Admission, Enrollment Agreement, High School Diploma or GED, Criminal Record Check, Child Abuse Clearance.
Program Overview

2019 Medical Assistant Graduates
Medical assistants play a critical role in the daily operations of medical offices, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. This CAAHEP accredited program prepares students to be multi-skilled members of the healthcare team. Students are trained in administrative, clinical, and laboratory procedures commonly performed by medical assistants. The curriculum provides students with the technical and interpersonal skills necessary to succeed in medical assisting. Training involves a mixture of classroom, laboratory, and clinical components to prepare the student for employment upon graduation. Graduates of this program meet AAMA requirements to take the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) exam.
Maximum # of Students Per Class: 24
Program starts in August. Please check with CPI Admissions and review the Program Enrollment Agreement for specific start dates.
Entry-Level Career Opportunities:
- Medical Assistant
- Medical Secretary
- Medical and Clinical Lab Technician
- Phlebotomist
Courses In This Program Include:
Course Descriptions
Anatomy and Physiology I, II
Anatomy and Physiology I &II introduces the student to basic knowledge of all body systems and their functions. Anatomy and Physiology also introduces common diseases and diagnostics /treatment modalities.
Medical Terminology
Medical Terminology is an introduction to the principles of medical word building to develop the necessary medical vocabulary used in health care settings. Students will study, analyze and interpret root words, prefixes and suffixes with emphasis on spelling, pronunciation, definition and use of medical terms.
Introduction To Healthcare And The Electronic Health Record
Introduction to Healthcare and the Electronic Health Record is designed to give the student a working knowledge of electronic health records. Students will learn the fundamentals of the systems used in various healthcare settings.
Pathways to Success with Integrated Technology
Pathways to Success with Integrated Technology assists students in developing skills necessary for success in higher education. Topics include transitioning to post-secondary learning, setting academic goals, time management/organization, study and test taking skills and utilizing electronic resources. This course is an introduction to fundamental skills such as composing documents, spreadsheets, and preparing presentations.
Introduction to Medical Billing
This course introduces health insurance and reimbursement. The student will learn principles of medical billing related to proper claim form preparation, submission and payment processing, and the follow-up process.
Medical Assisting/Clinical I, II, III
Clinical I is an introduction to basic skills, which includes assessment of vital signs, electrocardiography, aseptic/sterilization techniques, handling of biohazardous materials, identifying instruments, exam positions, and gathering medical information/charting. Clinical II is a continuation which includes patient interviews, developing communication techniques, setting up for office procedures, proper equipment operation, microscope and centrifuge skills, specimen collection, and administration of injectable medication. Clinical III is a continuation that includes identifying medical emergencies, first aid technique, and a review of CPR.
Medical Law & Ethical Principles In Health Care
Medical Law & Ethical Principles introduces medical ethics and related issues, such as legal guidelines and requirements for health care. Students will be taught to identify and respond to issues of confidentiality, perform within legal and ethical boundaries, and document appropriately. Ethical issues will be explored within the context of current laws and cases.
Medical Assistant/ Administrative I,II
These courses introduce the administrative duties performed in a medical office setting. This includes electronic filing, completion of medical insurance forms, operation of office equipment, billing & collection, and accounts receivable & payable.
Basic Pharmacology
Pharmacology addresses the medical assistant’s responsibility, the legal implications, and quality assurance in the administration of medications in the office setting. Focus is placed on knowledge of medications, dose calculations, and proper administration.
Technical Writing
Technical Writing introduces the practice of writing in a professional setting. This course is designed to help students apply concepts of effective written communication. This course will help the student develop the essential skills of a professional communicator with an emphasis on clear and effective written communication.
Basic Phlebotomy
Basic Phlebotomy addresses the following: Standard Precautions, Infection Control, specimen collection, and venipuncture.
Introduction to Medical Coding
This course introduces diagnostic (ICD-10CM) & procedural (CPT) coding as well as completion of insurance claims for a variety of health care insurance programs.
Clinical Practicum
Clinical Practicum provides students with the opportunity to correlate academic content with experiential learning. Students have the opportunity to apply knowledge and skills gained in the academic setting to the active delivery of services.
- Whole Number Operations
- Fraction Operations
- Decimal Operations
- Percent
- Number Comparisons and Equivalents
- Information and Ideas
- Rhetoric
- Synthesis
- Vocabulary
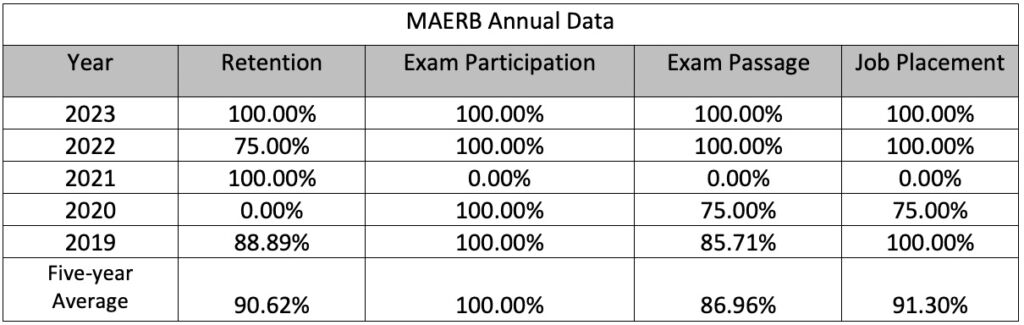
As part of CPI’s program accreditation requirements, The Medical Assisting Education Review Board (MAERB) requires that CPI post the program performance information annually. Below is CPI’s Medical Assistant Retention, Job Placement, Exam Pass Rate Performance and five-year average.